| Natural Language based Robot Programming | |
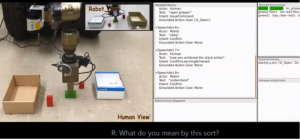 |
Robot have become significantly more powerful and intelligent, and are moving into more service oriented roles. As a result robots will more often be used by people with minimal technical skills and so there is a need for easier to use and more flexible programming systems. This research explores effective approaches towards teaching manipulation or navigation tasks to robots via natural language instructions. |
| Referential Grounding in Robotics | |
 |
A number of long-term goals in robotics (e.g., using robots in household settings) require robots to interact with humans. In this research, we explore how robots can correlate objects referred by natural language to the objects in the physical world sensed by an RGB-D camera, an area of research that falls under grounded language acquisition. |
| Visual Object Detection and Recognition | |
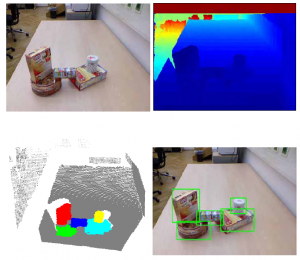 |
To improve the visual perceptual capabilities of robots, this research studies the problem of detecting and recognizing objects in possible ways such as active segmentation, attribute based recognition, interactive detection and recognition, etc. |
| Human-robot Interaction for Search and Rescue | |
 |
Search and rescue robot is a special type of mobile robot, for its application in the search and rescue works after nature or man-made disasters such as earthquake, hurricane, debris and mine collapse. In this research, we study the human-robot interaction methods to enhance the effectiveness and efficiency of search and rescue. |
| Dynamic Hand Gesture Recognition | |
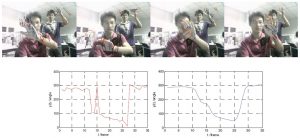 |
A novel method of dynamic hand gesture recognition based on Speeded Up Robust Features (SURF) tracking is proposed. The main characteristic is that the dominant movement direction of matched SURF points in adjacent frames is used to help describing a hand trajectory without detecting and segmenting the hand region. The dynamic hand gesture is then modeled by a series of trajectory direction data streams after time warping. Accordingly, the data stream clustering method based on correlation analysis is developed to recognize a dynamic hand gesture and to speed up calculation. The proposed algorithm is tested on 26 alphabetical hand gestures and yields a satisfactory recognition rate which is 87.1% on the training set and 84.6% on the testing set. |